Virulence factors of toxigenic corynebacteria
Host-pathogen-interaction: Functional analysis of proteins involved in pathogenicity of Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Corynebacterium ulcerans and Corynebacterium pseudotuberculosis
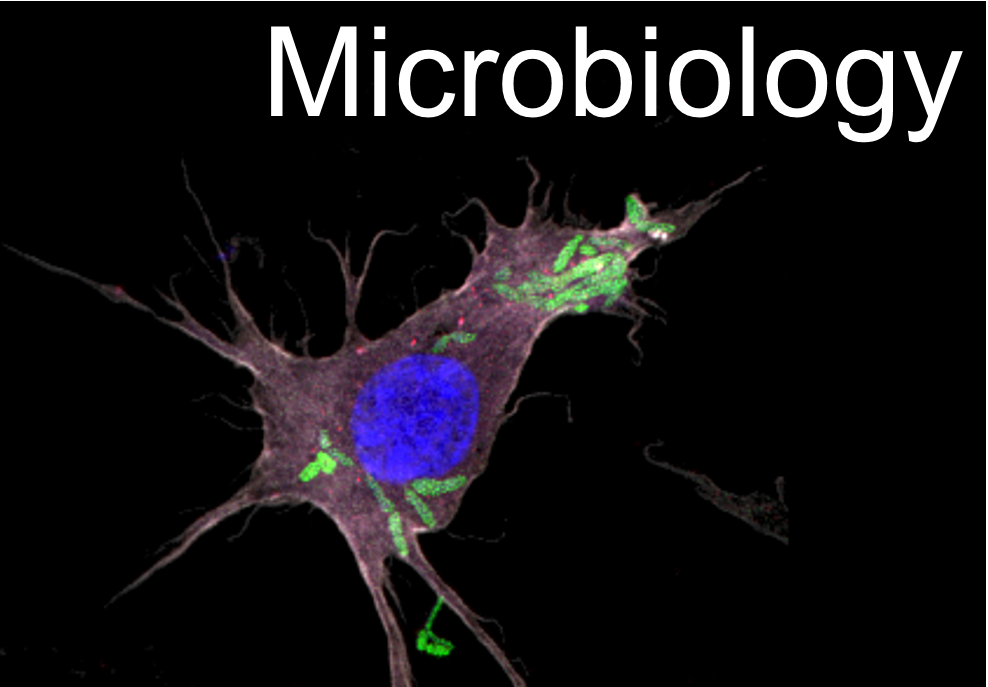
 SEM of C. diphtheriae ISS4060, C. ulcerans BR-AD22 and C. pseudotuberculosis FRC41 adhered to Detroit562 cells. Infection of Detroit562 cells with three different corynebacteria species for 90 min under cell culture conditions. Subsequently, cultures were fixed, dehydrated, sputtered with gold and examined using an FEI Quanta 200 scanning electron microscope (Ott, 2018).
SEM of C. diphtheriae ISS4060, C. ulcerans BR-AD22 and C. pseudotuberculosis FRC41 adhered to Detroit562 cells. Infection of Detroit562 cells with three different corynebacteria species for 90 min under cell culture conditions. Subsequently, cultures were fixed, dehydrated, sputtered with gold and examined using an FEI Quanta 200 scanning electron microscope (Ott, 2018).
Corynebacterium diphtheriae is the causative agent of diphtheria. During infection, this bacterium typically colonizes the upper respiratory tract. However, in the last years also an increasing number of skin infections were reported. We are especially interested in the function and evolution of virulence factors of this pathogen.
Interestingly, diphtheria and other infections are increasingly caused by Corynebacterium ulcerans. In the focus of our work related to this emerging pathogen, we are studying a ribosome binding protein with high structural similarity to Shiga-like toxins of enterobacteria and phospholipase D, a sphingomyelidase involved in macrophage interaction.